Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, affects millions of people worldwide, including many in Nigeria. It can occur at any age and, in many cases, can severely impact one's physical and mental well-being. Those who suffer from insomnia often experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and being unable to return to sleep. The consequences of inadequate sleep are profound, including impaired cognitive function, weakened immune response, emotional instability, and reduced overall quality of life.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of insomnia, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, referencing current research and clinical guidelines.
A deeper understanding of a condition can significantly aid in the recovery process, and that’s why we’ve provided this detailed explanation of insomnia. By understanding what insomnia is, its causes, and the ways you can support your own recovery, you are better equipped to take proactive steps towards better sleep.
This information is not only valuable for those directly affected by insomnia, but also for family members, friends, or colleagues who may have a loved one struggling with the condition. Sharing this article can help them understand the challenges of insomnia and how they can offer support during recovery.

Insomnia is defined as persistent difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep, or waking up too early and being unable to fall back asleep. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM), insomnia is categorized as either acute or chronic:
• Acute insomnia lasts for a short period, typically a few days or weeks. It is often triggered by temporary stressors, such as a major life event, illness, or jet lag.
• Chronic insomnia persists for at least three nights per week and lasts for three months or more. Chronic insomnia is a more complex condition and may be linked to other medical, psychological, or environmental factors.

The causes of insomnia are varied and can be classified into several categories, including psychological, physiological, environmental, and lifestyle-related factors.
Anxiety, depression, and stress are among the most common psychological causes of insomnia. Studies have shown that individuals with anxiety disorders experience heightened arousal, disrupting their ability to relax and fall asleep. Similarly, depression often co-occurs with insomnia, as changes in brain chemistry can impair sleep regulation.
• Anxiety:Individuals with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or panic disorder may struggle with sleep due to racing thoughts, hypervigilance, or physical tension.
• Depression:Depression can disrupt sleep patterns, often leading to either insomnia (difficulty falling asleep) or hypersomnia (excessive sleep).
Several physical conditions are linked to insomnia, including:
• Chronic Pain:Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and lower back pain can make it difficult for individuals to find a comfortable sleeping position, leading to fragmented sleep.
• Sleep Apnea:This condition involves repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, often leading to poor-quality sleep and daytime fatigue. Many individuals with sleep apnea may not realize their sleep is being disturbed.
• Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS):RLS causes an uncomfortable urge to move the legs, particularly when lying down or at rest, making it difficult for individuals to fall asleep.
• Hormonal Changes:Hormonal fluctuations related to menopause or pregnancy can disrupt sleep patterns.
The environment plays a significant role in sleep quality. Factors such as noise, light, temperature, and comfort can affect the ability to fall asleep or stay asleep.
• Noise:Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and lower back pain can make it difficult for individuals to find a comfortable sleeping position, leading to fragmented sleep.
• Light:This condition involves repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, often leading to poor-quality sleep and daytime fatigue. Many individuals with sleep apnea may not realize their sleep is being disturbed.
• Temperature:RLS causes an uncomfortable urge to move the legs, particularly when lying down or at rest, making it difficult for individuals to fall asleep.
Certain habits or lifestyle choices may increase the risk of insomnia:
• Caffeine and Nicotine:These stimulants interfere with sleep, particularly if consumed late in the day. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and sodas, can have a lasting effect on sleep if consumed too close to bedtime.
• Alcohol:Though it may induce drowsiness initially, alcohol disrupts deeper sleep cycles.
• Irregular Sleep Schedule:Frequent changes in sleep patterns can confuse the body's internal clock and worsen insomnia.
• Napping:Long or late-afternoon naps can make it harder to fall asleep at night, especially in individuals who are prone to insomnia
Some medications and withdrawal from substances like alcohol, caffeine, or nicotine can contribute to sleep disturbances.

The symptoms of insomnia can vary from person to person but commonly include:
• Difficulty falling asleep:These stimulants interfere with sleep, particularly if consumed late in the day. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and sodas, can have a lasting effect on sleep if consumed too close to bedtime.
• Frequent waking during the night:Though it may induce drowsiness initially, alcohol disrupts deeper sleep cycles.
• Waking up too early and being unable to return to sleep
• Daytime fatigue and irritability
• Mood disturbances, such as anxiety or depression:Chronic insomnia often leads to heightened stress, anxiety, and mood swings due to the lack of restorative sleep.
The effects of insomnia extend beyond just feeling tired. Insufficient sleep can have a range of negative consequences on both physical and mental health:
1) Cognitive Impairment:Chronic sleep deprivation impairs attention, memory, and decision-making abilities. Studies show that individuals with insomnia may experience slower reaction times and poorer performance in cognitive tasks.
2) Mental Health Issues:Insomnia is linked to anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions. It can both trigger and exacerbate these conditions.
3) Increased Risk of Chronic Illness:Long-term insomnia is associated with higher risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Poor sleep can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
4) Decreased Quality of Life:Insomnia reduces overall life satisfaction, affecting relationships, work performance, and emotional well-being. Chronic sufferers may also experience a decrease in motivation and social withdrawal.
Treating insomnia requires a multifaceted approach. Below are some of the most common and effective treatment options:
CBT-I is considered the gold standard for treating chronic insomnia. It addresses the root causes of insomnia by modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors.
a. Sleep Restriction:Limiting time spent in bed can help consolidate sleep.
b. Stimulus Control:Encouraging individuals to associate their bed with sleep, rather than other activities like watching TV or worrying.
c. Relaxation Techniques:Progressive muscle relaxation and mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety that contribute to insomnia.
Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT-I. For instance, research published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that CBT-I significantly improved sleep quality in patients with chronic insomnia compared to those who received standard medical care.
While medications can provide short-term relief, they are typically not recommended for long-term use. Some commonly prescribed medications include benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine sedatives.
• Benzodiazepines (e.g., lorazepam, temazepam):Limiting time spent in bed can help consolidate sleep.
• Non-benzodiazepine Sedatives (e.g., zolpidem, eszopiclone):Encouraging individuals to associate their bed with sleep, rather than other activities like watching TV or worrying.
• Antidepressants:Progressive muscle relaxation and mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety that contribute to insomnia.
• Melatonin Agonists:Medications like ramelteon work by mimicking the effects of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Medications should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. They may provide short-term relief but do not address the underlying causes of insomnia.
While medications can provide short-term relief, they are typically not recommended for long-term use. Some commonly prescribed medications include benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine sedatives.
• Sleep Hygiene:Regular sleep schedules, avoiding large meals before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
• Exercise:Regular physical activity can help improve sleep, but avoid vigorous exercise too close to bedtime.
• Mindfulness:Practicing relaxation techniques before bed can reduce stress and improve sleep quality.
Sleep 729 stands out because we offer tailored treatments designed specifically for you.
For instance, we may recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), which has proven highly effective for long-lasting insomnia. CBT-I helps identify the root causes of your sleep troubles and teaches you techniques to improve your sleep habits.
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, we may prescribe medications or suggest supplements to enhance your sleep quality.
What sets us apart is our commitment to your well-being. Our team regularly checks in with you to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
We provide ongoing support and offer valuable tips to help you achieve better sleep. This personalized approach can significantly improve your sleep quality and overall health.
If you're struggling with sleep, consider visiting our clinic for expert help.

If you're experiencing persistent sleep difficulties, it may be time to seek professional help. A sleep assessment can provide valuable insights into the root causes of your insomnia and guide you towards the most effective treatment options.
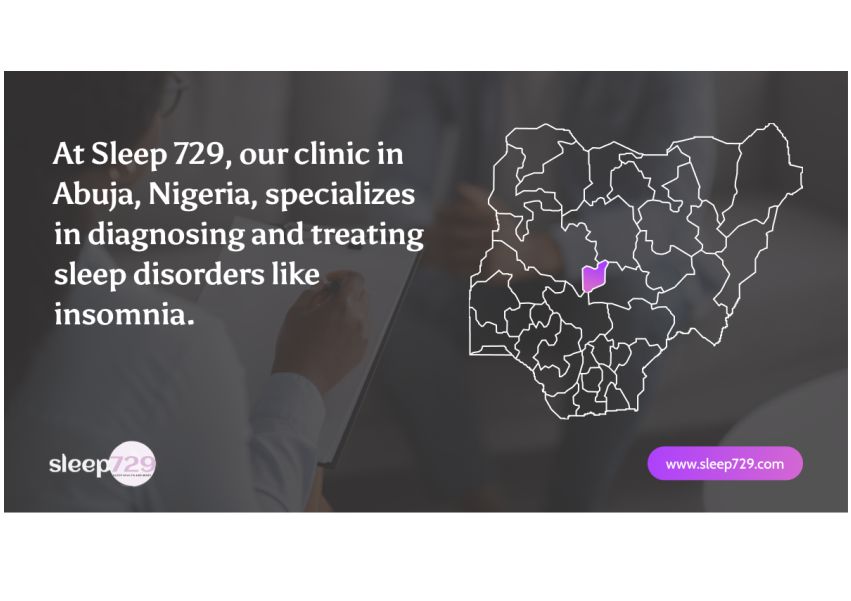
At Sleep 729, our clinic in Abuja, Nigeria, specializes in diagnosing and treating sleep disorders like insomnia. A sleep assessment with one of our experienced specialists can help you understand the underlying factors contributing to your sleep difficulties and set you on the path to better sleep and improved overall health.
If you're having trouble sleeping, it's a good idea to get help from professionals. Call Sleep 749 today on:
0906 757 7287
Don’t let insomnia control your life! Whether your sleep issues are new or long-standing, a comprehensive sleep assessment at Sleep 729 can provide the answers you need.
Our expert sleep specialists are ready to help you regain restful nights. Contact Sleep 729 in Abuja today and start your journey towards better sleep.
Call our clinic now for an appointment!

1. American Academy of Sleep Medicine. (2020). Insomnia. Retrieved from www.sleepeducation.org
2. Manber, R., & Carney, C. E. (2009). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia. In: "Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem," Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research.
3. Edinger, J. D., & Means, M. K. (2005). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia: A Meta-analysis of Treatment Efficacy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(3), 474-485.
4. Walker, M. (2017). Why We Sleep: The New Science of Sleep and Dreams. Scribner.
5. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (2023). Insomnia. Retrieved from www.ninds.nih.gov